Surprising Diagnosis in an Inflamed Prosthetic Joint
An 84-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with severe pain in her right knee. Her medical history was significant for stage 4 chronic kidney disease (CKD), hypothyroidism, aortic stenosis, mild cognitive impairment, osteoarthritis, and total arthroplasty of the right knee (performed in 2006).
Inspection of her right knee revealed a moderately sized, warm effusion and 3- × 3-cm area of erythema on her lateral knee with a well-healed scar from the previous surgery. Because of the potential consequences of septic arthritis, the patient was hospitalized and started on vancomycin, and plans were made to proceed with surgical washout.
Question: What surprising diagnosis did the medical team reach after treatment began?
Answer: Gout crystals were found in samples from a bedside fluid collection bag during irrigation of the knee.
Although it rarely presents in prosthetics, gout may be underdiagnosed, says Ryan Jessee, MD, a Duke rheumatology fellow who consulted on the case. “More than 30 cases of gout or pseudogout can be found in the literature for total knee arthroplasty, and approximately 4 cases of gout in hip replacement have been documented.”
In this case, new-onset knee inflammation led physicians to suspect she had septic arthritis of the prosthetic joint. Septic arthritis can cause mechanical disruption and hardware misalignment in prosthetic joints as well as life-threatening sepsis. Septic arthritis in a prosthetic joint is most often due to Staphylococcus aureus infection—similar to nonprosthetic joints.
Prosthetic joint infection is typically treated with surgical washout, but the patient experienced a stroke while in the hospital. Thus, she was not a good candidate for surgery because of its risks, Jessee says. As a safer alternative, orthopaedic specialists opted for bedside continuous irrigation of the knee with synovial fluid analysis.
During normal saline irrigation, white deposits were observed in samples taken from the fluid collection bag. Using polarizing microscopy, large, needle-shaped crystals displayed negative birefringence, a characteristic that confirmed the presence of gout crystals (Figure).
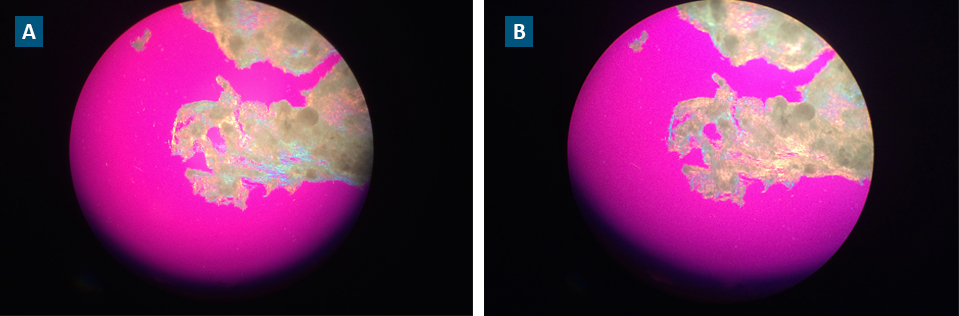
FIGURE. Visible negative birefringence used to diagnose gout. (A) Microscopy of gout crystals prior to and (B) following exposure to 90-degree polarized light
The patient’s inflammation improved while taking colchicine without antibiotics. The level of uric acid can often be artificially low during an acute flare, Jessee says, because of the uricosuric effects of inflammatory markers. As an outpatient, her uric acid level a few weeks later was above 10 mg/dL.
She was then started on low-dose allopurinol and daily prophylactic colchicine adjusted for her renal impairment to prevent flares. Her health care team plans to slowly up-titrate the allopurinol until her target uric acid levels are below 6 mg/dL.